News
Davos 2023 Tackles the Metaverse: 'The Next Era of the Internet Is Coming'
"The next era of the internet is coming," said a new report from the World Economic Forum (WEF) annual meeting, called Davos 2023 for its location in a resort area of Switzerland.
The WEF convenes leaders from government, business and other "civil society" institutions to address the state of the world and discuss priorities for the year ahead. The group says the meeting provides a platform to engage in constructive, forward-looking dialogues and help find solutions through public-private cooperation. It's widely viewed as an important gathering of leaders from all walks of life -- tech, politics, entertainment, journalism, economics, academics and many more -- who come together to hash out future initiatives.
Cutting-edge tech has been prominent at this year's meeting, which concludes tomorrow (Jan. 20). After showcasing Web3 predictions and a cryptocurrency rebound, the forum has tackled the metaverse, described as "an immersive, interoperable and synchronous digital world that will change how we interact, work and play."
That description comes in the Jan. 18 report, "Interoperability in the Metaverse," which was published with a companion report, "Demystifying the Consumer Metaverse."
Both reports constitute the initial findings of the WEF's "Defining and Building the Metaverse" initiative launched in May of last year. At the time, the WEF said it's "bringing together leading voices from the private sector, civil society, academia and policy to define the parameters of an economically viable, interoperable, safe and inclusive metaverse, focusing on two core areas: governance, and economic and social value creation."
Interoperability in the Metaverse
The interoperability report stems from the governance track, written in collaboration with Accenture and concentrating on providing topical guidance to empower metaverse stakeholders to lead responsibly while mitigating potential socioeconomic harms. The report said interoperability concerns:
- data circulating via interoperable infrastructures
- participants moving themselves, their assets and their creations across platforms and experiences
- experiences being safeguarded through collaboration and guardrails such as content moderation
Furthermore, the report said, interoperability in the metaverse can present enormous opportunities and value for frictionless experiences, development and economies. On the flip side, those "potential socioeconomic harms" include bad things like identity fraud and transaction fraud.
As shown in the graphic below, interoperability is one of the four metaverse value levers.
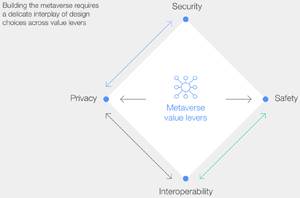 [Click on image for larger view.] Metaverse Value Layers (source: WEF).
[Click on image for larger view.] Metaverse Value Layers (source: WEF).
The report said the interoperability value lever can be used by stakeholders to:
- Improve access to participate, work and play in digital experiences and digital marketplaces
- Activate social, privacy, security and financial network effects
- Extend (real-life) experiences in novel ways to provide value to end-users
"Interoperability design choices must be balanced to create flexible systems that also consider privacy, security, safety, and identity needs," the report said. "Interoperability may not always be the desired state. While not inherently at odds, an action that only maximizes a single value -- such as interoperability -- may do so at the expense of achieving other goals. For example, over-indexing on interoperability without balancing safety as a value may expose children to unwanted content creating an imbalance between the desired levels of safety and privacy.
"Given the delicate interplay of design choices and value levers to pull -- standards, guidance, best practices, and other means should be timely and not be created independently. It is integral that stakeholders -- providers, creators, civil society and participants alike -- both formally and informally collaborate to co-develop human-first interoperability best practices and standards to maximize the potential of the metaverse at scale."
As another graphic shows, interoperability is also a primary key concept of the metaverse, taking equal billing along with Web3, extended reality (XR) and others:
 [Click on image for larger view.] Metaverse Key Concepts (source: WEF).
[Click on image for larger view.] Metaverse Key Concepts (source: WEF).
As far as the overall governance track that spawned the report, the WEF said these items will be helpful to consider when composing a future governance framework:
- The interoperable metaverse must be human-first to prioritize the well-being of all stakeholders
- Interoperability design must consider existing privacy, security and child-safety frameworks to strike the necessary balance
- Metaverse literacy is indispensable for enabling safe, interoperable experiences
- Interoperability design choices should be meaningful and timely
- Technical data interchange, participant engagement and management across experiences are dependent on multi-stakeholder collaboration
- Social contracts and participant expectations vary across experiences
- Interoperability is nuanced, multi-dimensional and is a spectrum that should be respected
The WEF said the report isn't meant to be a comprehensive view of the metaverse, but rather will be combined with other briefing papers to help compose a white paper on metaverse governance.
"Although harmonizing existing regulations and building new policy may prove necessary to adapt to new and unforeseen challenges, continued collaboration between metaverse stakeholders -- inclusive of providers, creators, civil society and participants -- and further research into policy, standards and other forms of guidance are a key first step towards progress in building a metaverse that is human-first," the report concluded. "Businesses, governments, academia and civil society should collaborate to build appropriate standards that support metaverse interoperability, encourage innovation and take a human-first approach. More work is to be done, but understanding the foundation that will drive interoperability, and the potential it can unlock, is an important first step."
Demystifying the Consumer Metaverse
Also written in conjunction with Accenture, this report focuses on consumer applications, presenting different use cases for consumer-facing organizations and applications in the metaverse.
This report decodes the metaverse -- specifically the confusing "web3" and "Web 3.0" components -- and discusses value creation, economic models and future value horizons.
"The metaverse is expected to have a wide-ranging impact on consumers' attitudes and behaviours, impacting how, where and when they will want to play, learn, earn and socialize in their existing reality or newly established augmented and virtual realities," the report said. "Consequently, organizations will need to redefine their brand image, shift their relationship model with consumers and change the way they monetize products and services in order to create true consumer value. They will likely move from offering products and services to being metaverse participants and providers, introducing engaging experiences and building communities in order to create meaning and fulfilment for their customers."
As far as those confusing web3 and Web 3.0 terms, the report said Web 3.0 describes the third stage of the internet, being an evolution focused on distributing systems to create a more secure, transparent and open internet experience that enables direct interactions between users and their peers without intermediaries.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Web 3.0 (source: WEF).
[Click on image for larger view.] Web 3.0 (source: WEF).
Meanwhile, web3 is how decentralization in this context is achieved, described as an emerging portfolio of decentralized technologies -- including: blockchain and its applications -- that work together with protocols and standards to establish provenance, veracity and value of data.
Key insights of the report as presented by WEF include:
- While it currently is difficult to define the metaverse, its main distinguishing components are highlighted to be social interaction, identity, multilateral value exchange and distribution, and a degree of immersion.
- Impacted by wider society -- organizations and individuals can take on one or multiple roles in the metaverse, from being participants to creators or providers.
- The role of individual creators will be amplified in the metaverse. Technologies such as AI and blockchain, will support this amplification. An evolving creator economy will influence value distribution in the metaverse greatly and offer far-reaching opportunities for businesses and individuals, but it will also pose challenges when approached incorrectly.
- Eight economic models were identified to drive value in the metaverse, including digital products and assets, access and influence, immersive commerce, payments and currency, asset monetization, advertising and marketing, the creator economy, and metaverse-native services.
- A selection of six drivers of metaverse growth and adoption were identified, including metaverse-ready networks, realistic avatars, infrastructure, governance, standards and regulation, ownership and artificial intelligence.
While this report is confined to the consumer metaverse and its economic challenges, further work within the WEF's value creation track will explore the enterprise and industrial metaverse, as well as the metaverse in the context of education, healthcare, life sciences, infrastructure and cities.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Defining and Building the Metaverse (source: WEF).
[Click on image for larger view.] Defining and Building the Metaverse (source: WEF).
As the above graphic shows, an examination of the industrial metaverse is next on tap in the WEF's value creation metaverse track, while the governance track discussed earlier will go on to examine: privacy, security and safety; identity; and a governance white paper.
"The next era of the internet is taking shape, with the convergence of technologies forging the metaverse, an immersive, interoperable, and synchronous virtual world," the report said. "Though a single standard definition for the metaverse has yet to emerge, experts agree that this new age of the internet will disrupt and transform current social and economic structures. From more immersive, empathetic social experiences to more universal access to services and education, the metaverse presents momentous opportunity, but also brings about new challenges."