News
Veeam Publishes Ransomware Trends Report, Debuts 'Data Cloud Vault'
Ransomware specialist Veeam Software announced a new cloud storage service to securely store backup data off-site in an always-immutable and encrypted format, just as the firm published a new ransomware trends report.
Unveiled today (June 4) during the company's VeeamON 2024 conference, the new Veeam Data Cloud Vault is a Microsoft Azure-based storage service that helps users securely store backup data. The service is designed to provide additional layers of protection for critical information.
The new offering, dubbed Veeam Vault in a news release, provides a pre-configured and fully managed cloud storage solution on Azure, addressing challenges faced by both enterprises and small/medium-sized businesses, the company said. Instead of handling their own cloud infrastructure, organizations can use Veeam Vault for secure data storage, management and access. The pricing includes not only storage but also API calls for writing and reading data. Users can access the service through Veeam's software interface and easily scale storage as needed, benefiting from reliability and disaster recovery capabilities.
The new solution, purpose-built to empower Veeam Data Platform users with the secure cloud storage needed for backups, was highlighted by the company as being:
- Secure: Safeguard data on Zero Trust storage that's immutable, encrypted and logically air-gapped from production.
- Easy: Access and use on-demand, fully managed Azure storage with zero configuration, management or integration complexities.
- Predictable: Eliminate bill shock with flat per TB pricing that meets an organization's needs today and tomorrow -- inclusive of API calls, restore and egress charges.
2024 Ransomware Trends Report
Veeam also today announced its 2024 Ransomware Trends Report, the third in the annual series. Based on a survey of 1,200 respondents including CISOs or similar titles and others whose organizations suffered at least one ransomware attack in 2023, it's designed to assess different perspectives in the fight against ransomware.
Some key findings from the report include data points that reveal 41 percent of data is compromised during a cyberattack, and that on average, only 57 percent of the compromised data will be recovered, leaving organizations vulnerable to substantial data loss and negative business impact as a result.
Other key findings of the report as presented by Veeam include:
- Cloud and on-premises data are just as easily attackable: Surprisingly, there was no significant variation between how much data was affected within the data center vs. data within remote offices/branch offices or even on data hosted in a public or private cloud. Meaning that as you've easily expanded your hybrid-cloud architecture to enable access to the users, that data is equally vulnerable to attacker. Hence, ensuring a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy across all those hybrid workloads is a must.
- Most organizations risk reintroducing infections: Alarmingly, almost two-thirds (63 percent) of organizations are at risk of reintroducing infections while recovering from ransomware attacks or significant IT disasters. Pressured to restore IT operations quickly and influenced by executives, many organizations skip vital steps, such as rescanning data in quarantine or a ‘sandbox', causing the likelihood of IT teams to inadvertently restore infected data or malware.
- Organizations must ensure recoverable data: As a "lesson learned," respondents of prior cyberattacks now recognize the importance of immutability with 75 percent of organizations now utilizing on-premises disks that can be hardened and 85 percent now utilizing cloud-storage with immutability capabilities. There is more work to be done, but this shows great progress in embracing a strategy that helps ensure that backups (instead of bitcoin) can be used to recover from ransomware.
Other individual data points pulled from the report include:
-
Backup repositories are a major target: In 96 percent of attacks, threat actors attempt to target backup repositories, highlighting the importance of robust backup security.
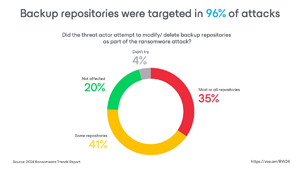 [Click on image for larger view.] Backup Repositories Were Targeted in 96 Percent of Attacks (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] Backup Repositories Were Targeted in 96 Percent of Attacks (source: Veeam).
-
Ransom is just a portion of the cost: While paying the ransom is a significant cost (32 percent of the financial impact), other factors like lost productivity and brand reputation take a bigger toll (68 percent).
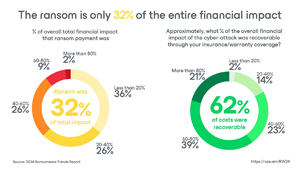 [Click on image for larger view.] Ransom Is Only 32 Percent of Entire Financial Impact (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] Ransom Is Only 32 Percent of Entire Financial Impact (source: Veeam).
-
Data recovery challenges: A significant portion of data (43 percent) is not recoverable after a ransomware attack, even after paying the ransom.
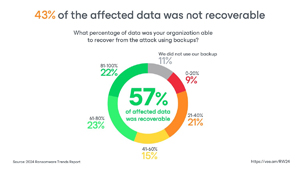 [Click on image for larger view.] 43 Percent of Affected Data Not Recoverable (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] 43 Percent of Affected Data Not Recoverable (source: Veeam).
-
Importance of clean backups: Only 37 percent of organizations ensure their backups are clean (free of malware) before restoring data, increasing the risk of re-infection.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Only 37 Percent Ensure Cleanliness During Restores (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] Only 37 Percent Ensure Cleanliness During Restores (source: Veeam).
-
Recovery options beyond original infrastructure: Organizations can recover data to cloud infrastructure (86 percent) or other on-premises servers (75 percent) in case the original servers are compromised.
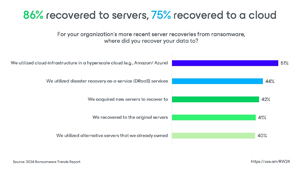 [Click on image for larger view.] 86 Percent Recovered to Servers, 75 Percent to Cloud (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] 86 Percent Recovered to Servers, 75 Percent to Cloud (source: Veeam).
-
Importance of collaboration: IT and security teams often lack alignment (63 percent need improvement), hindering overall preparedness.
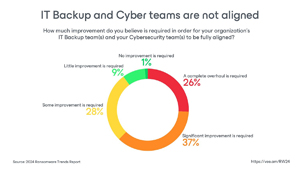 [Click on image for larger view.] IT Backup/Cyber Teams Not Aligned (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] IT Backup/Cyber Teams Not Aligned (source: Veeam).
-
Third-party involvement during remediation: Many organizations involve backup vendors (42 percent), security vendors (42 percent), and forensics specialists (42 percent) during remediation.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Third Parties Involved During Remediation (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] Third Parties Involved During Remediation (source: Veeam).
-
Wiping and restoring infected servers may not be an option: Due to various reasons, a significant portion (31 percent) of infected servers cannot be simply wiped and restored.
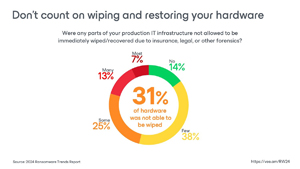 [Click on image for larger view.] Wiping and Restoring (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] Wiping and Restoring (source: Veeam).
-
Immutable backups gain traction: A growing number of organizations are using immutable backups (resistant to tampering) - 85 percent in cloud storage and 75 percent on disk.
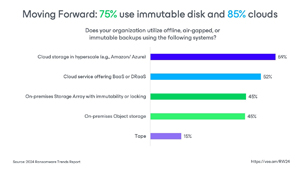 [Click on image for larger view.] 85 Percent Use Immutable Cloud Storage (source: Veeam).
[Click on image for larger view.] 85 Percent Use Immutable Cloud Storage (source: Veeam).
"Ransomware attacks will happen -- regardless of prevention technologies or employee awareness training," the report concluded. "Through the strategic alignment of IT and security teams and the implementation of robust security measures and technologies to ensure clean, secure, and recoverable backups, organizations will be better prepared to bounce forward from a ransomware attack by implementing the following best practices:
- Help IT teams and security teams work better together : One of the most revealing trends in this report is the fractured strategy, tool sets, and organizational alignment between executive leadership, the security teams responsible for prevention and detection, and the backup teams tasked with protection and recovery. In some organizations, especially those that handle large volumes of sensitive data, a cross-functional committee may oversee backup and disaster recovery planning. This committee typically includes representatives from IT, security, legal, and business units to ensure all perspectives are considered in the backup strategy.
- Plan ahead : The attack will be worse than you imagined and cost more than you're expecting. Organizations should make cyber preparedness plans that include broadening the use of immutable repositories, isolation and authentication of backup systems, and verifying the recoverability of the backups within the organization to ensure the established SLAs. Modern organizations should employ an incident response playbook or plan that allows for cross-team collaboration with the goal of utilizing a diversified immutable portfolio of disks, tapes, and clouds. And finally, being able to recover to both on-premises and cloud hosted infrastructure gives an organization its best potential to survive what could be an existential threat.
- Ensure your backups are clean and reliable : Similar to any disaster or cyber preparedness strategy, even daily backups require routine testing to ensure their viability on your worst day. For cyber resilience in particular, organizations need to test not only the recoverability of their backup data, but also the assurance of its cleanliness through immutable repositories.