News
Agentic AI Tops Gartner's 2025 Tech Trends
Agentic AI, wherein autonomous machine "agents" move beyond query-and-response generative chatbots to do enterprise-related tasks without human guidance, tops research firm Gartner's list of the top 10 tech trends for 2025.
 [Click on image for larger view.] 2025 Gartner Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends (source: Gartner).
[Click on image for larger view.] 2025 Gartner Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends (source: Gartner).
Of course, AI agents doing things on their own brings up fears of HAL 9000 and Terminator, for just two movie examples, and Gartner noted challenges in the space, advising that autonomous AI "Requires robust guardrails to ensure alignment with providers' and users' intentions," which could conceivably include not destroying humanity.
More realistic challenges that the firm has listed elsewhere include:
- Agentic AI proliferating without governance or tracking
- Agentic AI making decisions that are not trustworthy
- Agentic AI relying on low-quality data
- Employee resistance
- Agentic-AI-driven cyberattacks enabling "smart malware"
The business benefit, meanwhile, is: "A virtual workforce of agents to assist, offload and augment the work of humans or traditional applications."
The report follows moves by cloud giants Microsoft and Google in the field, reported yesterday in the article, "Microsoft and Google Turn to Autonomous AI Agents." It lists common enterprise use cases for agentic AI:
- Self-driving cars: These vehicles navigate roads, make driving decisions, and avoid obstacles without human intervention.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Autonomous software agents can handle routine business processes, such as data entry or email responses.
- Virtual Assistants: AI-driven personal assistants like Siri or Alexa execute commands, answer questions, and interact with users autonomously.
- AI in Video Games: Non-playable characters (NPCs) that adapt to player behavior, learning and modifying their tactics over time.
In fact, Gartner predicts that within four years, at least 15% of day-to-day work decisions will be made autonomously through agentic AI, up from basically 0% this year.
Those stats are fleshed out in the firm's What Is Agentic AI guidance: "Today's AI models perform tasks such as generating text, but these are 'prompted' -- the AI isn't acting by itself. That is about to change with agentic AI, or AI with agency. By 2028, 33% of enterprise software applications will include agentic AI, up from less than 1% in 2024, enabling 15% of day-to-day work decisions to be made autonomously."
Tom Coshow, senior director analyst, weighed in: "Organizations have long wanted to promote high-performing teams, improve cross-functional collaboration and coordinate issues across team networks. Agentic AI has the potential to perform as a highly competent teammate by providing insights from derivative events that are often not visible to human teammates."
While the above enterprise use cases were taken from general industry guidance, Gartner supplied its own for this report:
- Empowering workers to develop and manage more complicated, technical projects -- whether microautomations or larger projects -- through natural language
- Automating customer experiences by using data analysis to make highly calculated decisions at each step
- Changing decision making and improving situational awareness in organizations through quicker data analysis and prediction intelligence
It also supplied a graphic illustrating the growing disparity between AI systems that can act autonomously and traditional AI models that require explicit human inputs, those soon-to-be-primitive generative chatbots.
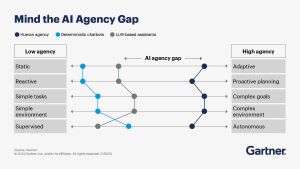 [Click on image for larger view.] Mind the AI Agency Gap (source: Gartner).
[Click on image for larger view.] Mind the AI Agency Gap (source: Gartner).
"AI agency is a spectrum," Gartner explained. "At one end are traditional systems with limited ability to perform specific tasks under defined conditions. At the other end are future agentic AI systems with full ability to learn from their environment, make decisions and perform tasks independently. A big gap exists between current LLM-based assistants and full-fledged AI agents, but this gap will close as we learn how to build, govern and trust agentic AI solutions."
With the fears of agentic AI running amok always present, though, it's no surprise that Gartner's No. 2 trend is AI governance platforms.
"AI is being used in more areas, especially in industries with strict regulations," the report stated. "As AI spreads, so do risks like bias, privacy issues and the need to align with human values. It's crucial to ensure AI doesn't harm certain groups, manipulate markets or control important systems." Or, again, destroy humanity.
The other eight trends include:
- Disinformation Security: Disinformation is a digital arms race: Phishing, hacktivism, fake news and social engineering are all being turbocharged by adversaries intent on sowing fear, spreading havoc and committing fraud. As AI and machine learning tools become more advanced and accessible, disinformation targeting enterprises is expected to rise, posing significant and lasting risks if left unchecked.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Quantum computing will soon become a reality, potentially within this decade, and is expected to render many conventional cryptographic methods obsolete, posing a significant risk to data security. Criminals are already anticipating this shift, adopting strategies like "harvest now, decrypt later," where they exfiltrate encrypted data with the expectation that they will eventually be able to decrypt it using quantum technology. This emerging threat has accelerated the need to prepare for PQC, which offers protection against quantum decryption.
- Ambient Invisible Intelligence: The technology for low-cost tags and sensors has become more affordable, making it economically attractive. It offers real-time visibility, which is valuable to organizations and supply chains -- and could expand into broader ecosystems over time. Advances in wireless standards like Bluetooth and cellular networks, as well as emerging technologies like backscatter and printed electronics, will support new use cases. This intelligence will also become a key data source for AI and analytics, improving products and processes.
- Energy-Efficient Computing: Sustainability is now a board-level focus. IT significantly contributes to environmental footprints, especially in industries like financial services and IT services, as energy-intensive technologies like AI drive higher energy consumption. While conventional processing improvements are reaching their limits, new computing technologies, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), neuromorphic computing and quantum computing, are expected to deliver the substantial energy-efficiency gains needed in the next five to 10 years.
- Hybrid Computing: Hybrid computing enables businesses to harness new technologies like photonic, biocomputing, neuromorphic and quantum systems for disruptive impact. GenAI is a key example, where solving complex problems requires advanced computing, networking and storage on a large scale.
- Spatial Computing: Spatial computing is trending due to advances in augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR) and AI technologies, enabling immersive digital environments across gaming, healthcare and e-commerce. The proliferation of 5G and new devices like Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 are driving consumer demand and opening opportunities for new business models. With major companies like Nvidia and Qualcomm building ecosystems, the market is projected to grow from $110 billion in 2023 to $1.7 trillion by 2033.
- Polyfunctional Robots: Polyfunctional robots are trending due to rising labor costs and the demand for improved ROI in industries like warehousing and manufacturing. Vendors are driving media attention with competitive price points, making advanced robotics more accessible. While there is a wide range of pricing and capabilities, early adopters are exploring the potential of these robots to handle multiple tasks, promising flexibility and cost-efficiency in businesses.
- Neurological Enhancement: Neurological enhancement is trending due to its potential to enable brain transparency, revolutionizing healthcare. As AI rapidly evolves, businesses are exploring brain-machine interfaces to help workers upskill and stay competitive by enhancing cognitive abilities. It's also being looked at to create deeper, personalized consumer experiences and interactions through next-generation marketing tactics.
Gartner said organizations can use the report to:
- Drill down on specific trends that Gartner predicts will change the shape of business
- See use cases from early adopters
- Consider how these innovations align with enterprise digital ambitions
- Anticipate how business and operating models might need to change
- Inform adjustments in mid- and long-term strategies and tech roadmaps
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.