How-To
Using the CROSH ChromeOS Command Line Interface
I have written a couple of different articles about ChromeOS Flex and FydeOS, both of which are based on ChromiumOS and allow you to run ChromeOS on x64 systems. I have found both to be helpful ways to repurpose older devices, especially those that do not support Windows 10, which will reach the End of Support (EOS) in mid-October 2025.
I found both operating systems easy to use and responsive on the decade-old laptops on which I installed and ran them. I could use them to check my email, run office applications, stream media, and browse the web.
I was born and raised with the command line, and it bothered me that I couldn't find a way to open a terminal and run commands. I appreciated the ability to navigate the file system, inspect the internals of an OS, execute commands, and write scripts to automate tasks that I needed to perform. It made sense that the developers didn't want to expose a command line, as the OS was designed to deliver applications and not act as a general-purpose OS.
Then I came across the Chrome OS Developer Shell (CROSH). CROSH is a powerful tool that provides a command-line interface for ChromiumOS. Unlike traditional terminals found in Linux or other OSes, CROSH is stripped down and tailored for ChromiumOS. It has tools that enable you to troubleshoot your system, manage network connections, monitor system performance, and interact with your hardware. CROSH is not designed for ordinary ChromiumOS users, but rather for developers, IT administrators, and advanced users who want to go beyond the graphical interface of ChromiumOS.
CROSH Commands
CROSH commands will be familiar to those who use Linux shells, as they are text-based commands that allow users to perform various tasks by interacting directly with ChromiumOS's underlying operating system. While ChromiumOS is built upon a Linux kernel, CROSH is distinct, with a subset of commands that differ slightly from Linux shell commands. CROSH is a set of commands relevant to the ChromiumOS ecosystem.
Accessing a CROSH Terminal
You can access a CROSH terminal by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+T.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
This will open a developer shell where you can enter commands.
CROSH Commands
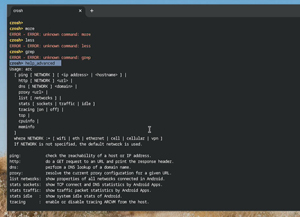
If you enter help at the prompt, you only get a terse message. To view a comprehensive set of CROSH commands, enter 'help_advanced'. Unfortunately, the commands "more," "less," and grep are not available, so I needed to use the mouse scroll button to page through the results.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
I looked at the commands and compiled a table summarizing some of the CROSH commands that I will use most frequently.
| Command |
Description |
| free | Display free/used memory. |
| ipaddrs | Display the IP addresses of the device. |
| route | Display network routing tables |
| ping [URL or IP] | Test network connectivity |
| tracepath | Trace the path to the network host. |
| top | Monitors active system processes |
| storage_test_1 | Perform a short offline SMART test on storage. |
| storage_test_2 | Perform an extensive readability test. |
| battery_test [seconds] | Checks battery performance |
| battery_firmware info | Display battery firmware |
| enroll_status | Device enrollment information |
| vmstat | Displays virtual memory usage |
| set_apn [APN] | Configures cellular settings |
| shell | Opens a Linux-style shell (requires Developer Mode) |
Using CROSH Commands
Using CROSH commands involves understanding their syntax, parameters, and expected outputs. For instance, the ping command is a standard tool for both Linux and Windows systems, as it can be used to investigate connectivity problems by sending packets to a server and measuring their response times.
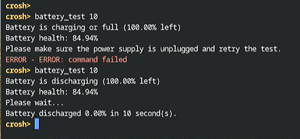
One of the more interesting CROSH commands is the battery_test command. It is used for checking battery health.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
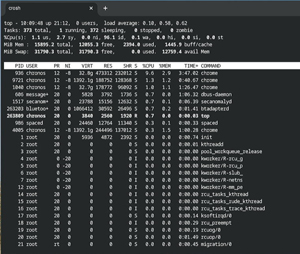
Top is a useful command-line utility designed to monitor system processes and resource usage in real-time. It provides detailed information about CPU usage, memory consumption, and running processes, enabling users to quickly identify performance bottlenecks or misbehaving applications. The interface is both dynamic and interactive, allowing users to see running processes, adjust priorities, or even terminate them directly from the command line.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
[Click on image for larger view.]
Final Thoughts
CROSH commands provide a shell and a way to explore the inner workings of ChromiumOS. Whether you're troubleshooting network issues, monitoring system performance, or exploring advanced developer options, CROSH is a vital tool for enhancing your ChromeOS experience.
You can read more about CROSH here.
About the Author
Tom Fenton has a wealth of hands-on IT experience gained over the past 30 years in a variety of technologies, with the past 20 years focusing on virtualization and storage. He previously worked as a Technical Marketing Manager for ControlUp. He also previously worked at VMware in Staff and Senior level positions. He has also worked as a Senior Validation Engineer with The Taneja Group, where he headed the Validation Service Lab and was instrumental in starting up its vSphere Virtual Volumes practice. He's on X @vDoppler.