News
Hackers Turn Kubernetes Machine Learning to Crypto Mining in Azure Cloud
When clouds get hacked, it's often the fault of user misconfigurations.
Just ask Amazon Web Services (AWS) about that. Beginning a few years ago or so, the AWS cloud notoriously suffered a long spate of such attacks, most of which leveraged misconfigured S3 storage buckets as attack vectors.
Recently, Microsoft's Azure cloud experienced a similar situation, this one concerning misconfigurations from lazy users of the Kubeflow machine learning platform used with Kubernetes, the wildly popular container orchestration system.
Hackers managed to exploit these misconfigurations to launch cryptocurrency mining campaigns leveraging powerful machine learning Kubernetes nodes, Microsoft announced earlier this month.
"Kubeflow is an open-source project, started as a project for running TensorFlow jobs on Kubernetes. Kubeflow has grown and become a popular framework for running machine learning tasks in Kubernetes. Nodes that are used for ML tasks are often relatively powerful, and in some cases include GPUs. This fact makes Kubernetes clusters that are used for ML tasks a perfect target for crypto mining campaigns, which was the aim of this attack," said Yossi Weizman, security research software engineer, Azure Security Center, in a June 10 blog post.
Crypto mining (or cryptocurrency mining or bitcoin mining) is a way to generate digital currency wealth by leveraging powerful computing power. While it's not illegal, it requires tremendous computing effort for usually minimal gains. The whole process is explained here.
The bad guys were able to turn Kubeflow machine learning to cryptocurrency mining by taking advantage of user misconfigurations having to do with dashboards deployed in Kubeflow clusters that expose Kubeflow UI functionality. Weizman summarized this:
The dashboard is exposed by Istio ingress gateway, which is by default accessible only internally. Therefore, users should use port-forward to access the dashboard (which tunnels the traffic via the Kubernetes API server).
In some cases, users modify the setting of the Istio Service to Load-Balancer which exposes the Service (istio-ingressgateway in the namespace istio-system) to the internet. We believe that some users chose to do it for convenience: without this action, accessing to the dashboard requires tunneling through the Kubernetes API server and isn't direct. By exposing the Service to the internet, users can access to the dashboard directly. However, this operation enables insecure access to the Kubeflow dashboard, which allows anyone to perform operations in Kubeflow, including deploying new containers in the cluster.
Microsoft's Azure Security Center earlier published a
Kubernetes Threat Matrix detailing the major techniques that are relevant to container orchestration security, with a focus on Kubernetes. Shading the matrix to illustrate the recent campaign results in this:
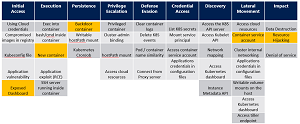 [Click on image for larger view.] The recent attack depicted in the Kubernetes Threat Matrix (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] The recent attack depicted in the Kubernetes Threat Matrix (source: Microsoft).
Weizman said the attack affected "tens of Kubernetes clusters" but there was no information provided about how much mining was conducted or if attackers managed to do other nefarious deeds via the exposed dashboards.
Although the Azure Security Center has detected similar campaigns against Kubernetes implementations that leverage exposed services to the internet as an access vector, this is the first Kubeflow-specific attack. For example, Weizman in April described a similar exploit of Kubernetes.
Weizman in his recent post advised organizations how to check to see if their clusters are impacted and provided advice going forward, warning that they should be aware of security aspects including:
-
Authentication and access control to the application.
-
Monitor the public-facing endpoints of the cluster. Make sure that sensitive interfaces are not exposed to the internet in an unsecure method. You can restrict public load balancers in the cluster by using Azure Policy, which now has integration with Gatekeeper.
-
Regularly monitor the runtime environment. This includes monitoring the running containers, their images, and the processes that they run.
- Allow deployments of only trusted images and scan your images for vulnerabilities. The allowed images in the cluster can be restricted by using Azure Policy.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.