News
Red Hat OpenShift 4.5 Integrates VMs with Containers, Serverless
Red Hat updated its open source, Kubernetes-based OpenShift application platform with a new OpenShift Virtualization platform, seeking to bring traditional virtual machines (VMs) into the modern cloud-native, container/serverless computing era.
Red Hat today (Aug. 17) announced Red Hat OpenShift 4.5, an open source container application platform based on the Kubernetes container orchestrator for enterprise app development and deployment. OpenShift is an on-premises platform as a service built around Docker containers orchestrated and managed by Kubernetes on a foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Today's v4.5 release features the general availability of OpenShift Virtualization 2.4, which was formerly called container-native virtualization. It lets enterprises run VMs within OpenShift, seeking to eliminate separate silos for development, management and operation of VM apps and container apps and serverless computing functions.
The new virtualization platform is based on the open source KubeVirt project, which was created by Red Hat and is now under the direction of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
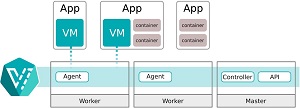 [Click on image for larger view.] KubeVirt: Making Virtualization Kubernetes-Native (source: Red Hat).
[Click on image for larger view.] KubeVirt: Making Virtualization Kubernetes-Native (source: Red Hat).
OpenShift Virtualization, Red Hat says:
- Enables organizations to modernize existing applications by running VMs, containers, and serverless functions side by side on a single Kubernetes-native architecture featuring bare-metal infrastructure
- Eliminates the silos between workflow and development that often exist in traditional application stacks
- Delivers the means to build, modify, and deploy applications residing in application containers and VMs in a common environment
- Helps organizations create and manage Linux and Windows VMs
- Connects to VMs through a variety of consoles and CLI tools
- Imports and cloned existing VMs
- Manages network interface controllers and storage disks attached to VMs
- Live migrates VMs between nodes
"By bringing new and existing applications to the same architecture, OpenShift Virtualization provides a consistent development experience and turbocharges an organization’s ability to deliver quickly on innovation," Red Hat said. "Once VMs are migrated to and managed by Red Hat OpenShift, they can be containerized over time, or be maintained as virtual machines. This allows users to develop and deliver hybrid applications built on containers and VMs to run side-by-side on the same platform."
As far as the general OpenShift 4.5 platform itself, the update sees a host of improvements to all aspects of the product, including vSphere, the company's cloud computing virtualization platform.
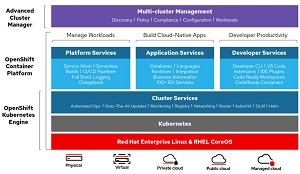 [Click on image for larger view.] OpenShift 4.5 (source: Red Hat).
[Click on image for larger view.] OpenShift 4.5 (source: Red Hat).
"With OpenShift 4.5, we are pleased to introduce support for OpenShift on vSphere with full stack automation experience (aka IPI). This is in addition to our existing support for vSphere with user provisioned infrastructure experience (UPI). OpenShift 4.5 also introduces support for running OpenShift clusters on Google Cloud using the pre-existing infrastructure installation model on a shared VPC," Red Hat said.
"For customers looking to deploy OpenShift 4 into resource-constrained environments like edge locations, OpenShift 4.5 adds support for compact 3-node clusters. This is now supported in bare metal deployments on OpenShift 4.5."
More information on OpenShift 4.5 can be found in the release notes and a blog post.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.