News
CNCF: Kubernetes Has 'Crossed the Chasm' to Become Mainstream
The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) has published its sixth annual cloud native survey, finding that Kubernetes has finally gone mainstream.
The 2021 Cloud Native Survey reveals that 96 percent of organizations are using or evaluating the technology, which has been fully embraced by large enterprises. In fact, the subhead of the survey reads: "The year Kubernetes crossed the chasm."
"Kubernetes adoption among the ever-expanding cloud native community is approaching 100 percent, meaning those investing in cloud native are strongly bought in and excited for the future," said Priyanka Sharma, executive director of the CNCF. "Our data also demonstrates how ubiquitous cloud native is, whether it is being deployed in-house or as a managed service. I believe 2022 will be a banner year for emerging areas of cloud native like edge, observability, and security as container infrastructures continue to mature both on the surface and under the hood."
The new edition is the first to include input from Datadog and New Relic, members of CNCF, and independent developer analyst SlashData, with the latter organization actually having previously teamed up with CNCF for series of developer-oriented cloud-native reports. Virtualization & Cloud Review covered this one from December 2021, which is mentioned in the new report.
"According to the most recent State of Cloud Native Development Report, developed for CNCF by SlashData, Kubernetes has demonstrated impressive growth over the past 12 months with 5.6 million developers using Kubernetes today," the report says. "This represents a 67 percent increase from a year ago when, adjusting for a change in the question methodology, there were 3.9 million Kubernetes developers worldwide. This group now represents 31 percent of all backend developers, an increase of 4 percentage points in the last year."
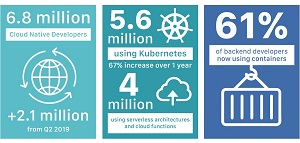 [Click on image for larger view.] Report Highlights from December 2021 Developer Report (source: CNCF/SlashData).
[Click on image for larger view.] Report Highlights from December 2021 Developer Report (source: CNCF/SlashData).
That data backs the first of three main takeaways from the report as presented by the CNCF:
- Container Adoption and Kubernetes has truly gone mainstream -- usage has risen across organizations globally, particularly in large businesses.
- With this de-facto status, Kubernetes is now going "under the hood" similar to Linux, with more organizations leveraging managed services and packaged platforms.
- CNCF is also starting to see organizations move up the stack -- adopting less mature projects to tackle challenges including monitoring and communications.
The "under the hood" reference pertains to Kubernetes becoming less visible, especially in organizations that are using serverless computing and managed services more, such that it becomes a ubiquitous, underlying container technology that users don't need to know that much about, like the Linux OS that's now baked into platforms and devices like phones and appliances.
"According to CNCF CTO Chris Aniszczyk, there is a growing void in understanding that Kubernetes and containers are essentially a package deal," CNCF said in an announcement of the survey. "Datadog reports that nearly 90 percent of Kubernetes users leverage cloud-managed services, up from nearly 70 percent in 2020."
The survey report backs that up by noting that 79 percent of respondents use certified hosted platforms, along with some more numbers:
"The discrepancies we've been seeing between those reporting container use (93 percent) versus Kubernetes use (96 percent) has been growing steadily over the past year -- there appears to be a growing void in understanding that these technologies are essentially a package deal," it says. "What's fascinating about this is how quickly Kubernetes has grown from a niche technology to something so utterly ubiquitous that folks don't even know they are using technologies built on it, as the value for end users has moved up the stack."
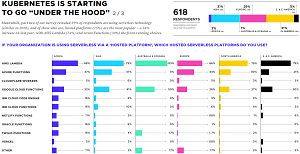 [Click on image for larger view.] Under the Hood (source: CNCF).
[Click on image for larger view.] Under the Hood (source: CNCF).
The "move up the stack" reference relates to organizations slowly leveraging Kubernetes APIs and interfaces such as runtime containers like CRI-O and containerd, and monitoring tools like Prometheus.
"However, just as Kubernetes has begun disappearing under the hood, awareness of wider cloud native technologies also seems to be dropping," the report says. "This is highlighted by the responses CNCF received when contrasted with production data from Datadog and New Relic -- which paint a more accurate picture of cloud native adoption.
"In the CNCF survey data we saw the use of our graduated projects in production and evaluation remain steady year-on-year. There were minor decreases in more mature graduated projects used in production which we attribute to the broader global responses from our growing community -- Fluentd saw a slight drop in production usage of 13 percent, followed by Envoy (-10 percent), and Prometheus (-6 percent). containerd saw the most significant rise in usage of 28 percent. However, this conflicts a bit with production data from observability companies which show an increase in mature projects such as Kubernetes and Prometheus."
 Project Adoption (source: CNCF).
Project Adoption (source: CNCF).
Here are some related data points:
- Argo, an open-source container-native workflow engine for Kubernetes, saw a 115 percent year-on-year increase in production use.
- Container runtime CRI-O saw in-production rise 51 percent year-on-year.
- New Relic reported a 43 percent overall increase in Prometheus adoption for the last six months of 2021, based on accounts.
- FluentD adoption grew by 53 percent over the past year based on data ingestion.
- Datadog reported the proportion of containerized companies that use containerd quickly grew 500 percent from 2020 to 2021.
- Containerized companies that use Envoy grew 39 percent from January 2020 to January 2021.
"This is an emerging trend, and it will be particularly interesting to contrast the results of CNCF's upcoming 2022 survey with what we are seeing today as the cloud native landscape continues to evolve," the report said.
Here's the methodology for the report:
The 2021 Cloud Native Survey was separated into two parts due to a large number of questions. Part one looked at containers and Kubernetes and was conducted between April and June 2021 with responses from 2,302 individuals. Part two, conducted between August and November 2021, covered cloud native technologies such as service mesh, serverless, and storage, as well as CNCF's other projects, and received 1,527 responses. To provide a more robust picture of how organizations are using cloud native technologies, the report incorporates production data from member organizations, including Datadog's 2021 Container Report and New Relic's O11y Trends Report. It also pulls in data from 'The State of Cloud Native Development' report, which was developed for CNCF by SlashData in 2020 and 2021.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.