News
What Workloads Hinder Enterprise Lift-and-Shift to Cloud?
A new hybrid cloud adoption survey reveals the workloads most responsible for holding back full enterprise IT cloud migrations.
That finding comes in the "challenges" section of a new survey-based hybrid cloud adoption report from Hornetsecurity.
Like many other similar reports, a lack of cloud talent -- specifically a "lack of technical knowhow or certified staff" -- was the No. 1 challenge reportedly blocking cloud adoption.
Unlike many other similar reports, this one asked which workloads were holding back cloud adoption, specifically which specific workloads respondents envisage remaining on-premises.
"The most common workload preventing IT departments from lifting all services to the cloud was 'Print & Imaging Services' (55 percent)," the company said in a March 10 news release. Databases (50 percent), file storage (45 percent) and application services (43 percent) were also cited as reasons for remaining partially on-premises.
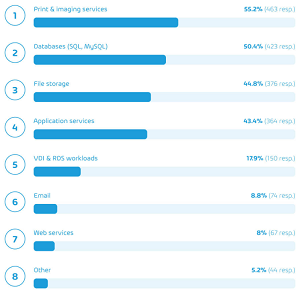 [Click on image for larger view.] Workloads Holding Full Cloud Adoption Back (source: Hornetsecurity).
[Click on image for larger view.] Workloads Holding Full Cloud Adoption Back (source: Hornetsecurity).
"With regards to 'print & imaging services' being the most frequently mentioned workload in the list, it's likely that many internal IT teams adopt an 'if it ain't broke, don't fix it' approach to this particular issue, especially since remote access for print services is redundant in most cases," Hornetsecurity said. "Print services are also a critical end-user service for many organizations, so IT departments likely exercise extra caution before attempting an upgrade so as not to interrupt operation. Databases and File Storage are also high on the list, with a combination of privacy and performance issues being the main reasons such workloads would remain on-premise for many companies. Industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, and others may also be playing a part, as 28.7 percent of respondents cited these as an obstacle for cloud adoption."
While the "Print & Imaging Services" reply might be surprising, some types of databases (the No. 2 answer) have been identified as being poor candidates for cloud migration, as reflected in guidance like "Workload Suitability Across Cloud and On-Premises Data Centers" from Nutanix in April 2021.
It listed the following as examples of workloads that aren't ideally suited to the cloud:
- Applications that interact at a low level with hardware and chips, or bound to proprietary hardware systems
- Certain large relational database management systems, which experience latency and other performance issues in the cloud
- Those that deal with sensitive health, telecom, or defense information
- Legacy applications that are incompatible with modern cloud architecture
That list even aligns in other ways with the Hornetsecurity findings.
"Among the reasons that our respondents cited behind having to keep certain workloads on premise, there were two that were more frequently mentioned than trust issues with the cloud," the Hornetsecurity study says. "These were 'legacy systems or software' and 'application compatibility,' each being reported by 51.8 percent and 39.5 percent of respondents respectively. This would indicate that even though Microsoft and other cloud platform providers have placed significant resources into providing avenues for IT professionals to modernize their applications and assist in the migration to hybrid cloud architecture, this effort hasn't resulted in the elimination of related issues.
"In fact, when asked what technical difficulties respondents have with cloud technologies, the most common answer provided (48.2 percent) was 'technical knowhow or certified staff.' Meaning that even though the technology required to overcome issues related to legacy software and application compatibility are available, many businesses lack the required knowledge and skill to implement them. There is further evidence of this lack of knowledge, as one third (33.3 percent) of respondents also cited connectivity as a technical difficulty they have with cloud technologies. Indeed, while connectivity is definitely one of the most challenging aspects of the application of cloud platforms, it can be handled with the correct knowledge and certification."
Other highlights of the report include:
- 67 percent of respondents believe that a hybrid cloud strategy is not a stepping stone but a permanent destination
- 34.1 percent of respondents said that "privacy trust issues with the public cloud" are keeping certain workloads on-premises
- Only 5.7 percent of respondents reported no technical difficulties with cloud or hybrid technologies
- The most popular containerization services are: Docker (30.7 percent); Azure Kubernetes Service - in Azure (22 percent); Azure Container Instance (19.2 percent); Kubernetes (17.9 percent); VMware Tanzu (9.2 percent); Azure Kubernetes Service - on Azure Stack HCI (5.4 percent); Other (32 percent)
The report is based on a survey of more than 900 IT professionals primarily based in North America and Europe, with no survey date range provided.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.