News
Cloud Security Alliance AI Report Goes 'Beyond the Hype'
As AI gains traction across enterprise IT, a new report from the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) provides empirical evidence of how AI agents can improve Security Operations Center (SOC) performance.
Titled "Beyond the Hype: A Benchmark Study of AI Agents in the SOC," the research benchmarks how AI tools--specifically Dropzone AI's autonomous SOC agent--affect speed, accuracy, completeness, and analyst attitudes during simulated investigations.
"This study evaluated the impact of AI SOC agents on security analyst performance in simulated Security Operations Center (SOC) alert escalations," the report said. "This study focused on escalated alert investigations where humans are needed to validate a malicious finding. The goal was to measure the impact of AI assistance on SOC analyst investigative speed, accuracy, and consistency compared to manual methods."
The study involved 148 participants in SOC and incident response roles. Participants were randomly assigned to either a control group using traditional tools (AWS GuardDuty and Microsoft Sentinel) or an AI-assisted group using Dropzone AI. Each participant completed two scenarios: an AWS S3 bucket alert involving unauthorized access and a Microsoft Entra failed login alert suggesting a credential-stuffing attempt. The research measured performance metrics such as investigation speed, accuracy, and completeness, as well as analysts' confidence, perceived difficulty, and attitudes toward AI in cybersecurity.
"Analysts using Dropzone AI also demonstrated greater consistency across multiple investigations and reported positive perceptions of the platform," CSA said. "Notably, 94% of participants said their view of AI in cybersecurity became more positive after hands-on use."
Across every measure, analysts using AI assistance outperformed their manual counterparts, completing investigations faster, with greater accuracy and more detailed reporting--while also maintaining confidence and a positive view of AI technology. Here's a look at the report's four key takeaways as they were highlighted by CSA.
SOC Analysts Achieve Faster and More Accurate Investigations with AI Assistance
According to the study, AI-assisted analysts completed investigations 45% faster in the first scenario and 61% faster in the second. Accuracy was also significantly higher--97% vs. 86% for the first scenario, and 85% vs. 81% in the second.
This demonstrated that AI agents like Dropzone AI can streamline complex investigative workflows without sacrificing correctness.
This chart visually compares the time-to-completion averages between AI-assisted and manual analysts, highlighting substantial efficiency gains:
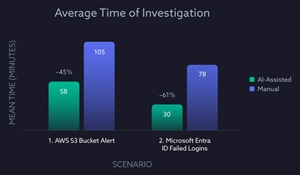 [Click on image for larger view.] Average Time of Investigation (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] Average Time of Investigation (source: CSA).
These findings suggest measurable operational value for organizations handling high alert volumes, where speed and precision are critical.
AI Tools Sustain Investigative Completeness and Detail, Even as Workloads Increase
The research also measured completeness and documentation quality using a seven-point rubric of key investigative steps. Completeness scores declined 29% for manual users but only 16% for AI-assisted participants.
Likewise, manual users' report lengths decreased by 20-27%, while AI-assisted users maintained or slightly increased their level of detail.
This chart illustrates how AI users sustained completeness under simulated alert fatigue conditions:
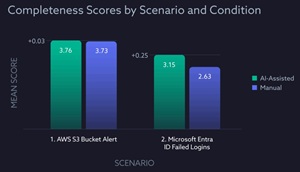 [Click on image for larger view.] Completeness of Investigation (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] Completeness of Investigation (source: CSA).
This indicates that AI systems can help analysts maintain rigor and consistency as cognitive load increases, a common challenge in real-world SOC environments.
Analysts Maintain Confidence in Their Findings While Embracing AI in Cybersecurity
Despite the performance boost, participants using AI tools did not exhibit inflated confidence or lower perceived difficulty. Both groups rated confidence between 3.6-3.7 on a four-point scale and difficulty between 2.4-2.6, indicating that improved results stemmed from genuine efficiency rather than overreliance on automation.
This chart shows comparable confidence levels across both conditions, reinforcing that AI assistance enhanced outcomes without creating false assurance:
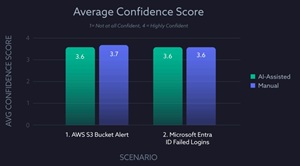 [Click on image for larger view.] Confidence Levels (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] Confidence Levels (source: CSA).
These results suggest that AI can complement, rather than distort, human judgment in SOC investigations.
Positive User Experience Reinforces AI's Potential for Rapid Adoption in SOC Environments
User sentiment toward AI tools was overwhelmingly favorable. Among AI-assisted participants, 94% reported a more positive view of AI after the study, with an average recommendation score of 8.7 out of 10 and a Net Promoter Score (NPS) of 53.
Descriptors most frequently chosen by participants included "Efficient," "Helpful," "Time-saving," and "Intuitive."
This infographic summarizes this feedback, visually showing that 100% of users labeled the tool efficient:
 [Click on image for larger view.] Feedback (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] Feedback (source: CSA).
The combination of high satisfaction, low negative feedback, and minimal learning curve points to strong potential for rapid AI adoption across SOC teams seeking immediate operational benefits.
CSA's overall conclusion underscores these trends: AI-assisted analysts performed investigations more accurately, more quickly, and with greater consistency than manual counterparts. The report frames AI as a practical accelerator for SOC operations rather than a speculative technology, signaling that AI augmentation is now a measurable force reshaping cybersecurity workflows.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.