News
Cloudera Study Finds Data Privacy Top Concern as Orgs Scale Up AI Agents
As organizations race to integrate AI agents into their cloud operations and business workflows, a new report from Cloudera highlights a crucial reality: while enthusiasm is high, major adoption barriers remain. Chief among them is the challenge of safeguarding sensitive data.
AI agents are a hot topic in advanced GenAI development because they move beyond simple prompt-and-response models, enabling autonomous reasoning, decision-making, and multi-step task execution -- effectively turning AI from a passive tool into an active collaborator.
With AI agents increasingly embedded in core IT systems, customer interactions, and infrastructure optimization, concerns about data privacy have emerged as the top issue holding organizations back, says the new report from Cloudera, which sells a hybrid platform for data, analytics, and AI. Before companies can fully realize the transformative potential of agentic AI, they must first build trust that these autonomous systems can handle critical enterprise data securely and compliantly.
"When asked to rank their top concerns in adopting AI, respondents pointed to data privacy concerns (53%), followed by integration with existing systems (40%) and high implementation costs (39%)," says "The Future of Enterprise AI Agents, published April 16. "These findings illustrate that trust and compatibility issues are primary roadblocks, as enterprises worry about safeguarding sensitive data and transforming legacy environments."
 [Click on image for larger view.] Key AI Agent Challenges (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Key AI Agent Challenges (source: Cloudera).
Here's a summary of top challenges to AI agent adoption:
- Integration Complexity (40%): Many enterprises find it extremely challenging to integrate AI agents into existing legacy systems and cloud architectures.
- High Costs (39%): Beyond the initial investment, scaling and operationalizing AI agents require significant spending on infrastructure, security, and skills development.
- Lack of Expertise (34%): Organizations struggle to find or train staff capable of building, deploying, and managing agentic AI effectively at scale.
- Ethical and Regulatory Concerns (32%): Enterprises are worried about AI agents making biased decisions or taking actions that could violate compliance or ethical standards.
- Governance Concerns (30%): There's widespread recognition that without strong accountability frameworks, autonomous agents could act in ways that are hard to monitor or control.
"To be fair, 37% of surveyed enterprises report that integrating AI agents into current systems and workflows has been very or extremely challenging," the report said. "This finding points to integration as a pain point for large organizations with complex IT ecosystems. In other words, deploying AI agents is not a plug-and-play endeavor. For this reason, deploying and managing agentic AI demands skilled professionals and proper infrastructure. The most effective way for organizations to begin leveraging agentic AI is by evaluating their existing infrastructure to ensure it meets the necessary requirements, focusing on data management, security, and compliance standards. Equally important is training teams to effectively manage and deploy AI agents, starting with small-scale implementations to assess their impact before expanding on a larger scale."
What's more, the report further explored bias, fairness, ethics and AI governance. It indicates agentic AI has the potential to transform user experiences and business operations, but it also carries the risk of undermining consumer and employee trust. When AI is trained on historical data, it can reinforce societal biases unintentionally and influence outcomes. AI bias has already negatively impacted real-world workplaces. The report then fleshes out actual examples in healthcare and defense.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Trustworthy AI Principles (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Trustworthy AI Principles (source: Cloudera).
The report emphasizes that bias, fairness, and AI governance are non-negotiable, indicating that organizations should prioritize lifecycle audits, transparency, and ethical design to maintain trust as agent deployments scale.
The report is based on a survey of nearly 1,500 enterprise IT leaders across 14 countries that was conducted to understand their adoption patterns, use cases, and sentiments around AI agents.
As far as that enthusiasm goes, the report shows that over the past two years, enterprise adoption of AI agents has surged, with 57% of organizations beginning implementation during that period -- including 21% that did so within just the last year. This rapid shift underscores how agentic AI has moved swiftly from early concept to operational reality, fueled by major technological advances between 2023 and 2024. For many enterprises, AI agents are no longer optional experiments but are now seen as essential tools for sharpening competitiveness and accelerating return on investment.
"Consequently, expansion plans for agentic AI are nearly universal," the report said. "An overwhelming 96% of respondents plan to expand their use of AI agents in the next 12 months, with half aiming for significant, organization-wide expansion."
Unsurprisingly, just as data privacy was the chief concern holding back enterprise AI agent adoption, strengthening it was the No. 1 goal of IT leaders looking for improvements in AI agents.
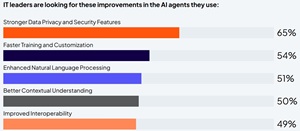 [Click on image for larger view.] Stronger Data Privacy and Security Features Wanted (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Stronger Data Privacy and Security Features Wanted (source: Cloudera).
Other highlights of the report include:
- 2025 is the tipping point for AI agent adoption: Enterprises are moving from pilot projects to full-scale, organization-wide deployments.
- AI agents are seen as the natural evolution of GenAI investments: 85% of organizations say prior GenAI adoption has paved the way for agentic AI integration.
- Cloud-native and hybrid architectures are critical: Most enterprises prefer building agents close to their private or hybrid cloud infrastructure for security and flexibility reasons.
- Open-source LLMs are surging: Open models are challenging proprietary options by offering better cost-efficiency, deployment flexibility, and data sovereignty.
- Most popular early use cases are customer support, process automation, and predictive analytics: Enterprises are focusing on domains where AI agents can deliver fast, measurable ROI.
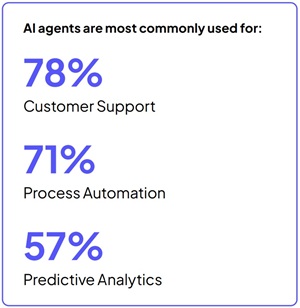 [Click on image for larger view.] Use Cases (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Use Cases (source: Cloudera).
Here's a summary of Cloudera's recommendations for 2025 agentic AI adoption:
- Strengthen your data foundation and integration capabilities: Enterprises should modernize their data architecture and unify platforms to securely handle the scale and complexity AI agents require, ensuring consistent controls for privacy and compliance.
- Start with high-impact projects to deliver immediate ROI, and grow from there: Begin AI agent adoption in low-risk, high-value areas like internal IT support or customer service, where impact is measurable and implementation is manageable, then scale gradually.
- Establish accountability first, and then build governance and ethics frameworks: Clearly assign responsibility for AI agent behavior and outcomes before deploying at scale, then implement systems for auditing, transparency, and bias mitigation throughout the agent lifecycle.
- Upskill teams and foster a culture of human-AI collaboration: Train employees not just in building and managing agents, but also in understanding how they reason and operate, encouraging continuous learning and collaboration across technical and business teams.
The report is based on a survey of 1,484 enterprise IT leaders conducted in February 2025 across 14 countries. Respondents included CIOs, CTOs, and senior IT decision-makers responsible for AI strategy and deployment. The research spans multiple industries -- including finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and telecommunications -- to provide a broad view of how organizations are adopting and expanding the use of AI agents.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.