News
AI Permeates, Cloudera Study Says, Mostly in the Cloud
Cloudera has released new findings on enterprise AI adoption, showing that cloud infrastructure is central to the shift from experimentation to almost complete integration. The report, in conjunction with previous company studies, illustrates how enterprises are scaling AI initiatives across hybrid environments while navigating challenges of security, governance, and data access.
"In just the past year, artificial intelligence (AI) has surged from a strategic priority to an urgent mandate for business leaders," is the opening line of the study. "No longer confined to pilot programs or future forecasts, AI is now reshaping operations, redefining workflows and rewriting the rules of competition. IT leaders now see AI not just as a tool, but as a force multiplier -- capable of unlocking hidden opportunities, accelerating efficiencies, and empowering our workforce hungry for the next era of productivity."
AI Adoption Now Mainstream
Titled "The Evolution of AI: The State of Enterprise AI and Data Architecture," Cloudera's brand-new survey of more than 1,500 IT leaders reveals that 96% of enterprises have integrated AI into core business processes, up from 88% in 2024. Of these, 21% said AI was fully embedded, and 54% reported significant integration. Respondents noted real returns, with 52% reporting measurable business value and only 1% not seeing results.
About that 96% figure, a related Cloudera news release published Sept. 25 said: "This is up from 2024, when 88% of survey respondents said they were currently using AI within their companies. This indicates that AI has gone from experimentation to full integration in core processes and workflows. And it's paying off: 70% of respondents said they have achieved significant success with AI initiatives, with only 1% having yet to see results."
Hybrid Cloud Data Architectures
Cloud choices are shaping AI strategies. The survey found that 63% of organizations store data in private cloud, 52% in public cloud, and 42% in data warehouses. Many enterprises also continue to rely on on-premises systems, including mainframes (38%) and distributed environments (32%). Nearly one-quarter reported using data lakehouses, with efficiency and governance cited as key benefits.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Cloud Storage (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Cloud Storage (source: Cloudera).
This hybrid approach is seen as critical for scaling AI. When asked about its advantages, respondents cited security (62%), improved data management (55%), and improved analytics (54%). Cloudera noted that success hinges on being able to "bring AI to data wherever it resides--public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises--while ensuring full governance, lineage, and trust."
Technical and Security Challenges
Enterprises reported persistent technical hurdles. Data integration was identified as the top limitation (37%), followed by storage performance, compute power, and lack of automation (each 17%). Cost pressures have also grown: 42% of IT leaders now cite training compute costs as too high, up from 8% last year.
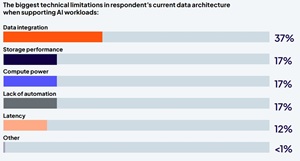 [Click on image for larger view.] Technical Limitations (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Technical Limitations (source: Cloudera).
Security concerns remain high. Half of respondents cited data leakage during model training, 48% noted unauthorized data access, and 43% pointed to insecure third-party AI tools. Despite these risks, 76% of leaders expressed strong confidence in their organization's ability to secure AI-related data.
 [Click on image for larger view.] Security Concerns (source: Cloudera).
[Click on image for larger view.] Security Concerns (source: Cloudera).
"While those concerns linger for AI security, Cloudera's survey found that many feel confident in their organization's ability to secure data used in AI systems," the report said. "Among respondents, 24% said they were extremely confident, 53% noted they were very confident, and 19% felt somewhat confident. This is supported by a year-over-year shift in views around securing organizations' data landscapes. In 2024, this was a factor that 66% of respondents said was the biggest challenge, whereas in 2025, that number declined to 54%. "
Regional Differences in Cloud Adoption
Cloud adoption patterns vary by geography. In the U.S., 74% of respondents said they store data in private cloud and 62% in public cloud. In the U.K., private cloud usage was higher at 82%, while in Brazil it reached 90%. These preferences also influence perceptions of hybrid cloud benefits: U.S. and U.K. respondents emphasized security, while Brazilian leaders ranked flexibility higher.
What's Next
Looking ahead, enterprises see operational efficiency (29%), customer experience (18%), and product innovation (15%) as the areas most likely to deliver AI returns in the next year. Cloudera emphasized that meeting these goals requires platforms capable of applying AI to 100% of enterprise data, across clouds, on-premises, and the edge.
"Enterprise leaders are more confident in their data, said Cloudera in a Sept. 25 blog post. "AI is becoming deeply integrated into core processes, transforming everything from operational efficiency to customer experience. But many still have yet to make all of their data accessible to AI. This gap in access within data architectures poses serious risks from a competitive standpoint but also means AI initiatives may not be as effective as they otherwise could be.
"Maximizing the value of AI is critical for the long-term outlook of enterprises, particularly as they seek to scale the technology. Overcoming these challenges starts with understanding internal data needs and prioritizing partners and tools that help bring AI to data anywhere, wherever that data resides."
And More
Cloudera's new study follows an earlier 2025 report (see "Cloudera Study Finds Data Privacy Top Concern as Orgs Scale Up AI Agents").
Here's a summary of top challenges to AI agent adoption from that earlier 2025 report:
- Integration Complexity (40%): Many enterprises find it extremely challenging to integrate AI agents into existing legacy systems and cloud architectures.
- High Costs (39%): Beyond the initial investment, scaling and operationalizing AI agents require significant spending on infrastructure, security, and skills development.
- Lack of Expertise (34%): Organizations struggle to find or train staff capable of building, deploying, and managing agentic AI effectively at scale.
- Ethical and Regulatory Concerns (32%): Enterprises are worried about AI agents making biased decisions or taking actions that could violate compliance or ethical standards.
- Governance Concerns (30%): There's widespread recognition that without strong accountability frameworks, autonomous agents could act in ways that are hard to monitor or control.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.