News
Ransomware Variants Exploded in Past 6 Months: Threat Report
One takeaway from Fortinet's latest edition of its semiannual Global Threat Landscape Report is a remarkable upsurge in ransomware variants in the past six months.
The new report for the first half of 2022 is based on data from the company's global array of sensors monitored by its FortiGuard Labs threat intelligence and research unit.
The explosion in variants is traced to increasingly organized ransomware actors who are enabled by the efforts of technically proficient attackers who sell ready-to-go offerings to less-sophisticated "script kiddie" types in an approach that might be called Ransomware Inc.
"Ransomware attacks continue to become more sophisticated and aggressive, with attackers introducing new strains and updating, enhancing, and reusing old ones, Fortinet said in an Aug. 17 blog post listing key findings of the 1H 2022 FortiGuard Labs Threat Landscape Report.
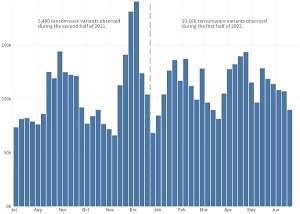 [Click on image for larger view.] Weekly Ransomware Volume Over the Last 12 Months (source: Fortinet).
[Click on image for larger view.] Weekly Ransomware Volume Over the Last 12 Months (source: Fortinet).
"What's especially troubling as we look at the first half of 2022 is that the number of new ransomware variants we identified increased by nearly 100 percent compared to the previous six-month period," the post continued. "Our FortiGuard Labs team saw 10,666 new ransomware variants, compared to just 5,400 in 2H 2021. This explosive growth in ransomware can be mainly attributed to Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) becoming increasingly popular on the dark web. Cybercriminals are using subscription-model services and purchasing plug-and-play ransomware to achieve a quick payday."
Fortinet last year published a post that further discussed the increased organization, stating: "Cybercrime has become big business, replete with call centers that assist their victims to pay ransoms, tech support, affiliates who move and launder money, and those who manage forums on the Dark Web to create and sell code."
In discussing malware delivery mechanisms, the report shed light on tactics, techniques and procedures, or TTPs, where defense evasion remains the top attack tactic globally. Defense evasion refers to steps taken by attackers to hide their presence after hacking into a system.
"Examining adversarial strategies reveals takeaways about how attack techniques and tactics are evolving," Fortinet said. "FortiGuard Labs analyzed the functionality of detected malware to track the most prevalent approaches over the last six months. Among the top eight tactics and techniques focused on the endpoint, defense evasion was the most employed tactic by malware developers. They are often using system binary proxy execution to do so. Hiding malicious intentions is one of the most important things for adversaries. Therefore, they are attempting to evade defenses by masking them and attempting to hide commands using a legitimate certificate to execute a trusted process and carry out malicious intent."
 [Click on image for larger view.] Top Malware Tactics and Techniques (source: Fortinet).
[Click on image for larger view.] Top Malware Tactics and Techniques (source: Fortinet).
As the graphic above shows, system binary proxy execution was the top technique found, referring to the process of executing a command or executable through the use of digitally signed -- or otherwise trusted -- binaries, thus proxying execution of malicious content.
"Looking at the top eight tactics and techniques from the past six months of EDR [endpoint detection and response] telemetry, defense evasion is the top tactic employed by malware developers," the report said. "They are also the most likely to use system binary proxy execution to do so. Hiding malicious intentions is one of the essential things for malware developers to master, so it makes sense that they would try to mask their malware by using a legitimate certificate to hide commands to evade a business's defenses. Process injection, where the criminal works to inject code into a process to evade defenses, is the second most popular technique we've seen over the past six months."
Other highlights of the extremely detailed, lengthy report as presented by Fortinet include:
- OT Devices and Endpoints are Still Irresistible Targets:"While the pandemic forced organizations to create comprehensive work-from-anywhere (WFA) security strategies, remote work still presents a serious risk. While endpoints remain one of an attacker's top targets, vulnerabilities don't just exist in the IT space -- they're also increasingly being found in operational technology (OT) products. While OT technologies aren't new, they present a growing opportunity for cyberattacks as organizations continue to converge their IT and OT networks."
- Wipers are Widening Their Foothold Across Borders: "Analyzing wiper malware data reveals a disturbing trend of cybercriminals using more destructive and sophisticated attack techniques -- in this case, using malicious software that destroys data by wiping it. In the first six months of 2022, FortiGuard Labs identified at least seven significant new wiper variants used by attackers in various targeted campaigns against government, military, and private organizations. This number is important because it's nearly as many total wiper variants as have been publicly detected in the past 10 years. While we saw a substantial increase in the use of this attack vector in conjunction with the war in Ukraine, the use of disk-wiping malware was also detected in 24 additional countries."
- Integrated Security Solutions Powered by AI are a Must: "The increase in the breadth and frequency of cyberattacks translates into more cyber risk for organizations, which means security teams need to be just as nimble and methodical as their adversaries. Outdated point-product approaches to security are insufficient, making integrated security solutions essential to combatting this proliferation of advanced and sophisticated attacks. Organizations need tools that can ingest real-time threat intelligence, apply AI to detect threat patterns and correlate massive amounts of data to detect anomalies, and automatically initiate a coordinated response across networks. This holistic approach to a cybersecurity mesh architecture allows for much tighter integration and increased automation, making it easier for security teams to coordinate quickly and respond effectively to threats in real time."
"Cyber adversaries are advancing their playbooks to thwart defense and scale their criminal affiliate networks," said Derek Manky, an exec at FortiGuard Labs. "They are using aggressive execution strategies such as extortion or wiping data as well as focusing on reconnaissance tactics pre-attack to ensure better return on threat investment. To combat advanced and sophisticated attacks, organizations need integrated security solutions that can ingest real-time threat intelligence, detect threat patterns, and correlate massive amounts of data to detect anomalies and automatically initiate a coordinated response across hybrid networks."
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.